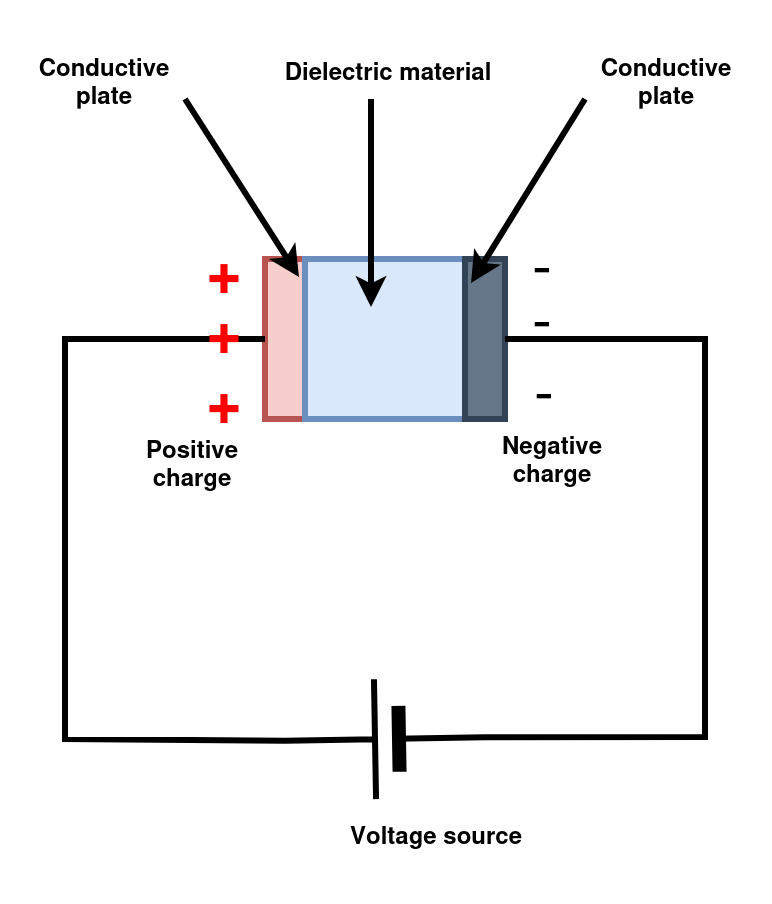
Capacitors serve as indispensable components in electronic circuits, playing a vital role in storing and releasing electrical energy. The fundamental structure of a capacitor comprises two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across these plates, an electric field is created. This leads to the accumulation of positive and negative charges on each plate. In this article we explore the common types of capacitors, their distinguishing characteristics, and their applications.
Dielectric materials used in capacitors
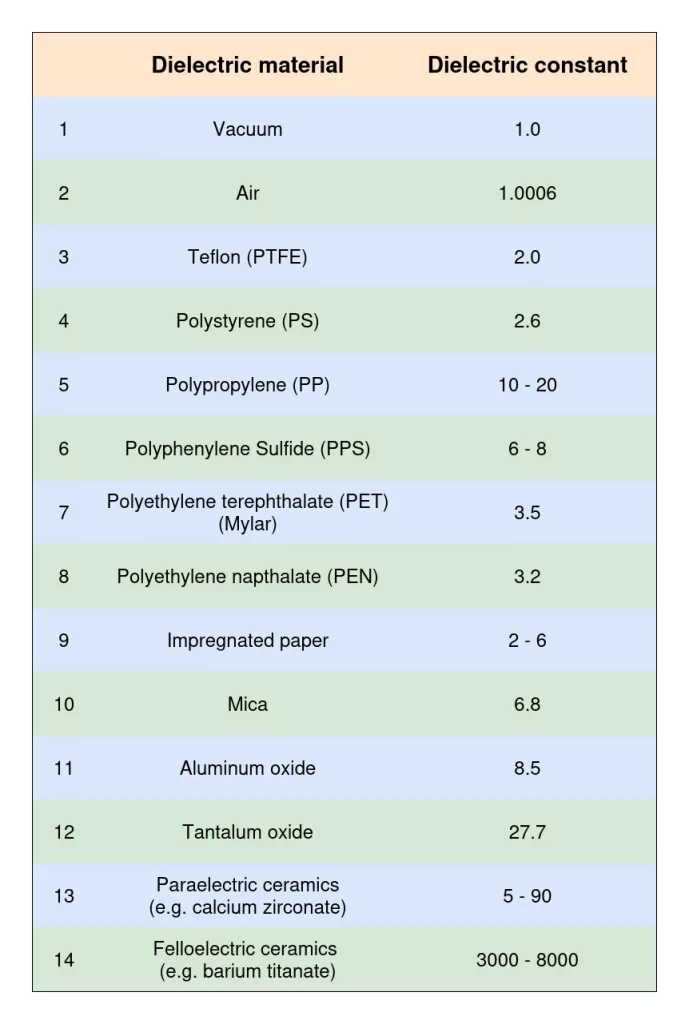
The properties of a capacitor are greatly determined by the dielectric material used. But what is a dielectric material? A dielectric material is an insulating substance placed between the plates of a capacitor. This insulating medium influences various characteristics of a capacitor, including capacitance, voltage rating, insulation resistance, case size, and energy storage efficiency. Table 1 shows the dielectric constants of commonly used dielectric materials.
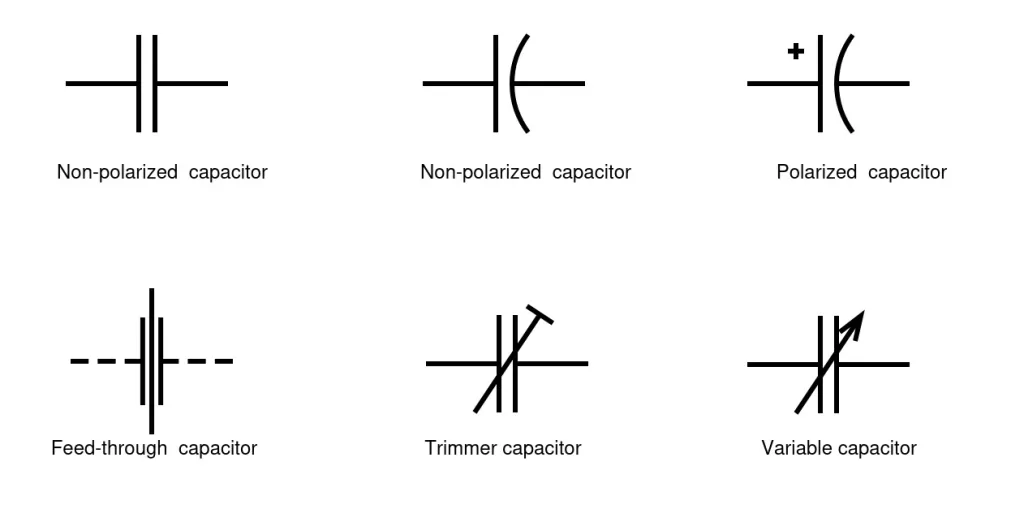
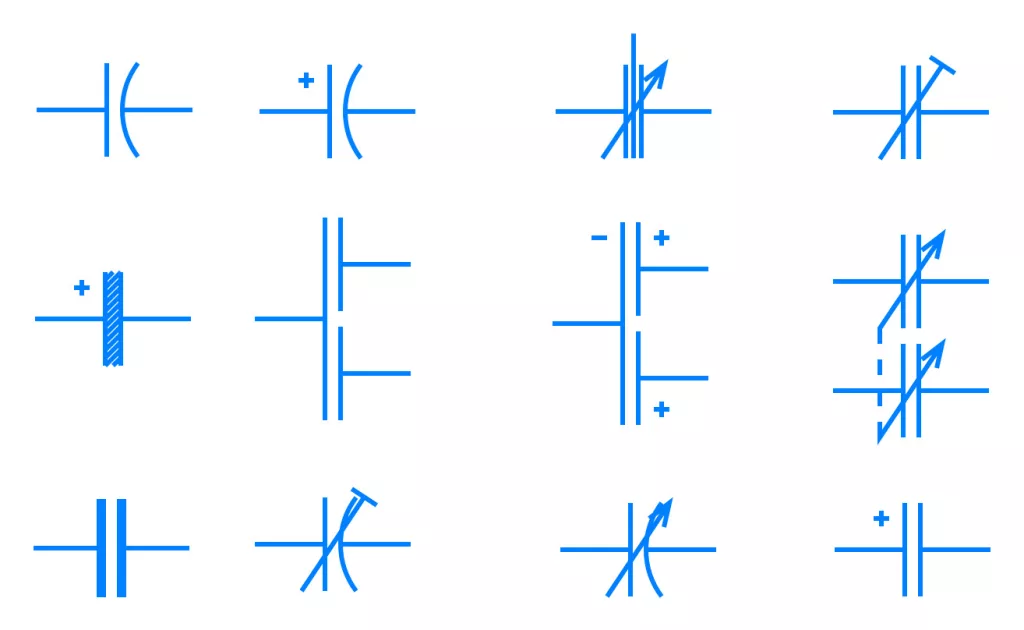
Capacitor symbols for various capacitor types
In electronic circuits, capacitors are denoted using different symbols. Each capacitor symbol communicates the type of capacitor and whether it is polarized or not. Figure 2 shows common capacitor symbols that you can find in schematics and circuits.
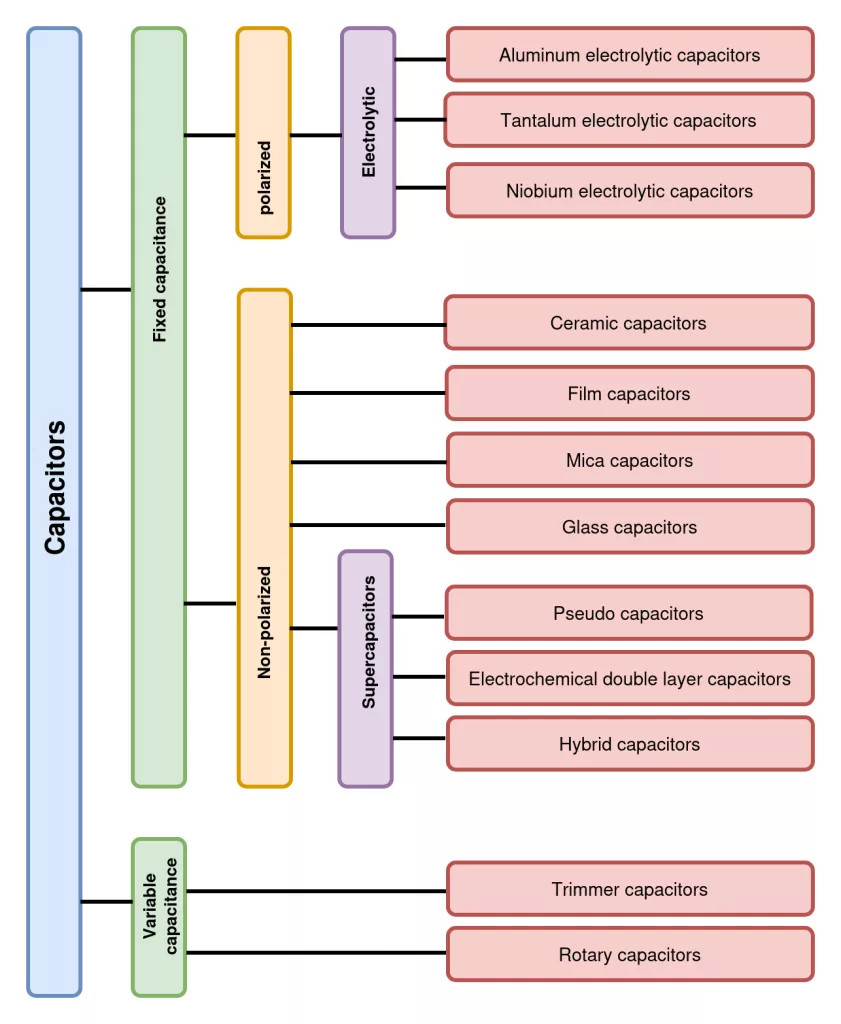
Common types of capacitors
Capacitors can be broadly categorized into two classes: variable capacitance and fixed capacitance capacitors. The main types of fixed capacitance capacitors include ceramic, aluminum electrolytic, tantalum, film, and mica capacitors. Figure 3 shows classification of the common types of capacitors.
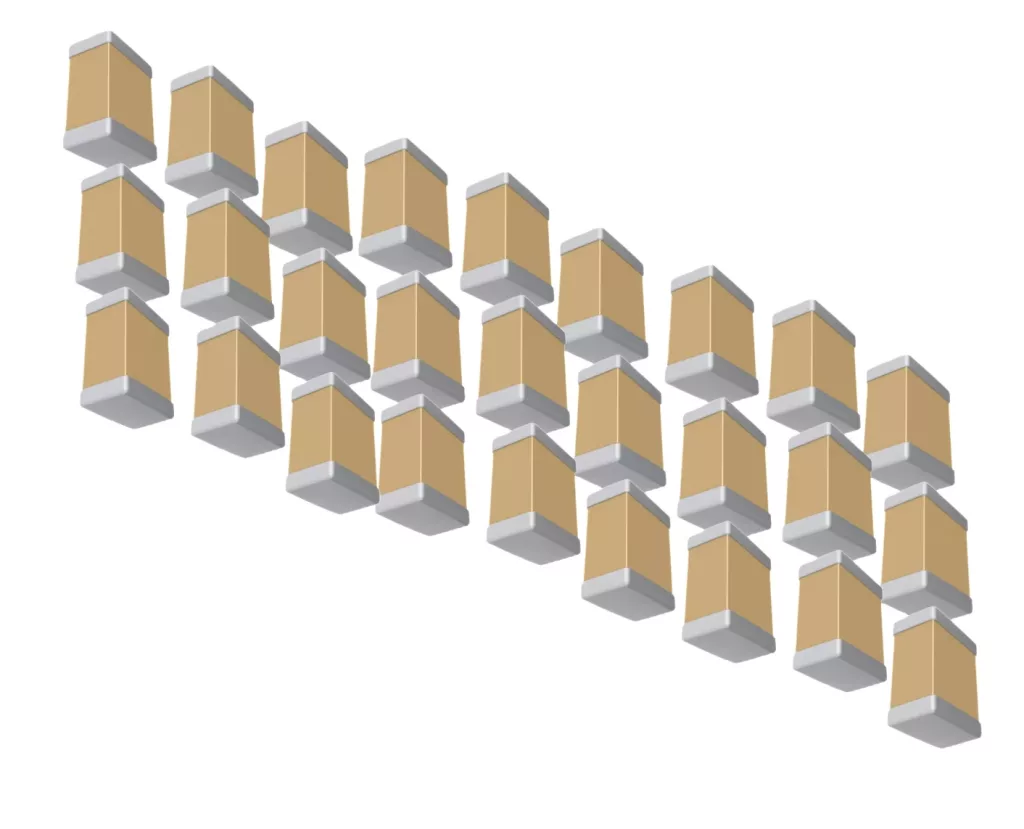
Ceramic capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are versatile components and they are used in a wide range of applications. These capacitors utilize a ceramic material as the dielectric between their conductive plates. Ceramic capacitors are recognized for their adaptability and stable performance across varying temperatures. In addition, these capacitors are available in a broad range of capacitance values.
Owing to their versatility, ceramic capacitors have become integral to electronic designs. They are widely used in decoupling, filtering and even precision timing applications. Their compact size and high-frequency response also make them ideal for applications in radio frequency (RF) circuits and microwave systems. Understanding the nuances of ceramic capacitors is essential for those seeking to optimize the performance of their circuits.
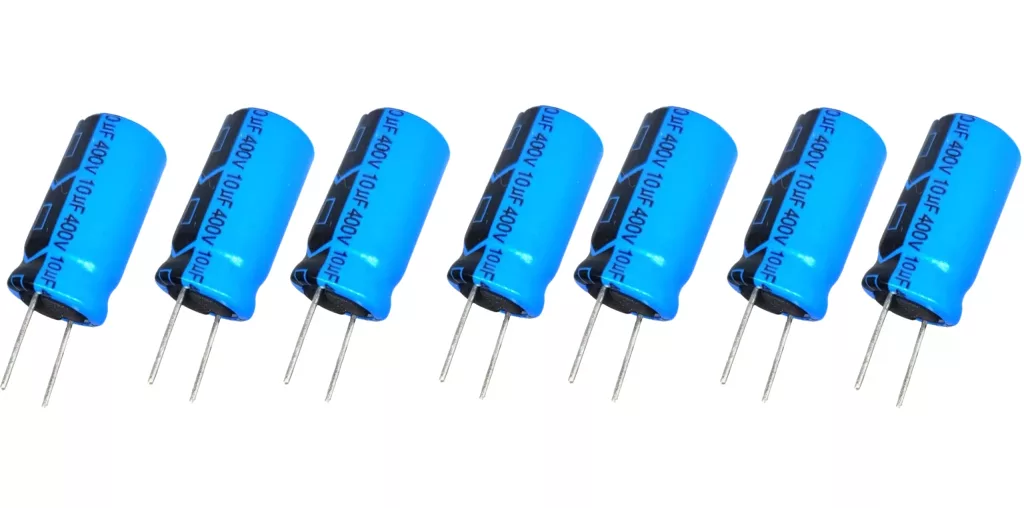
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance and play a crucial role in energy storage. These capacitors derive their name from the electrolyte that serves as the dielectric, usually in liquid or gel form. What sets electrolytic capacitors apart is their ability to store a significant amount of energy, making them indispensable in applications where bulk capacitance and efficient energy storage are paramount.
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are commonly used in power supply circuits and audio systems. This is mainly due to their capability to provide an energy reservoir for consistent and reliable electronic operation. On the flip side, these electrolytic capacitors are polarized, and special attention is required when installing them.
Tantalum capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer very low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and leakage current. These passive components feature tantalum metal as one of the plates and a tantalum oxide layer as the dielectric. This combination yields relatively high capacitance in a component with a compact size. The impressive volumetric efficiency of these components makes them ideal for use in portable electronic devices.
The high capacity and low leakage of tantalum capacitors make them suitable for sample and hold applications. They also find use in general timing applications. The high reliability of these components makes them a good choice for some medical and space applications. Compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum capacitors are pricier. Additionally, similar to other polarized capacitors, reversing the polarity of these capacitors can easily lead to their destruction.
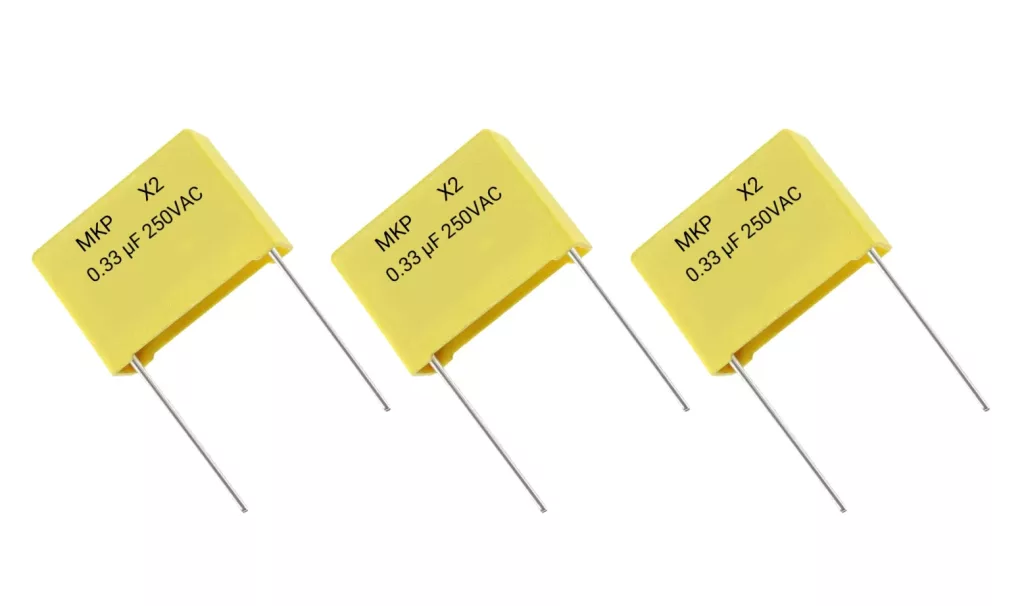
Film capacitors
A typical film capacitor consists of a thin plastic film sandwiched between metal foil plates. These capacitors offer impressive stability and reliability which make them ideal for diverse applications. Additionally, the thin dielectric film allows for precise control over the capacitance. This characteristic makes film capacitors a preferred choice in applications that demand accuracy.
Film capacitors come in a variety of types including polyester, polypropylene, polyethylene, polycarbonate and Teflon. In today’s circuits, these capacitors are commonly used for filtering, timing circuits, and applications where dependable performance is crucial. Furthermore, film capacitors are widely used in audio systems and other applications requiring high precision.
Conclusion
In summary, capacitors come in a variety of types, each with unique characteristics. Each type of capacitor—ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, and film—plays a crucial role in electronic design. Ceramic capacitors excel in adaptability, electrolytic capacitors shine in energy storage, tantalum capacitors offer space efficiency, and film capacitors provide reliability. For engineers and hobbyists, understanding these components is key to designing systems that deliver the required performance and reliability.

Pingback: A guide to various tantalum capacitor types and their uses -
Pingback: A Guide to Characteristics and Uses of Silver Mica Capacitors -
Pingback: A Guide to Types and Applications of Supercapacitors -